In our fast-evolving digital world, the demand for skilled tech professionals is skyrocketing. As technology advances, new roles are created and existing ones evolve, making the job market dynamic and ever-changing. This guide explores 10 technology jobs predicted to be in high demand over the next ten years, detailing their key responsibilities, required skills, and real-life examples of professionals excelling in these fields.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning Specialists
AI and machine learning are now crucial across many industries, including healthcare and finance. AI specialists develop algorithms and machine learning models to analyze large datasets, automate processes, and provide valuable insights.
Skills Needed: Proficiency in programming languages like Python, data analysis, statistics, neural networks, and deep learning frameworks.
Example: A machine learning engineer at Netflix optimizing recommendation algorithms to enhance user engagement.
 2. Cybersecurity Analysts and Ethical Hackers
2. Cybersecurity Analysts and Ethical Hackers
With the rise of cyber threats, cybersecurity is a top priority for organizations globally. Cybersecurity analysts and ethical hackers play essential roles in protecting digital assets and mitigating security risks. They assess network vulnerabilities, conduct penetration tests, and implement security measures.
Skills Needed: Strong analytical abilities, knowledge of cybersecurity frameworks and tools, and the ability to think like attackers.
Example: Cybersecurity analysts at Google work to strengthen defenses against evolving cyber threats.
3. Data Scientists and Analysts
In the age of big data, data scientists and analysts are vital for extracting actionable insights from complex datasets. They collect, clean, and analyze data using statistical techniques, machine learning algorithms, and data visualization tools.
Skills Needed: Proficiency in R or Python, expertise in data mining and machine learning, and strong business acumen.
Example: A data scientist at Airbnb analyzing user behavior data to optimize pricing strategies.
4. Cloud Computing Specialists
The rapid adoption of cloud computing is driving demand for professionals who can design, deploy, and manage cloud-based infrastructure and services. Cloud computing specialists, including cloud architects and engineers, help organizations enhance scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency.
Skills Needed: Expertise in cloud platforms like AWS or Microsoft Azure, virtualization, networking, and security.
Example: Cloud solutions architects at Adobe Systems optimizing cloud environments for SaaS applications.
5. Software Developers and Engineers
Software development remains at the core of technological innovation, with a constant need for skilled developers to create software solutions. Software developers and engineers build applications, websites, and systems using languages like Java, JavaScript, or C++.
Skills Needed: Collaboration with cross-functional teams, translation of requirements into software features, and ensuring scalability and performance.
Example: Software engineers at SpaceX developing mission-critical software for spacecraft and launch vehicles.
6. DevOps Engineers
DevOps practices aim to streamline software development and deployment through automation, collaboration, and CI/CD pipelines. DevOps engineers bridge the gap between development and operations, enabling faster release cycles and improved software quality.
Skills Needed: Expertise in automation tools like Jenkins or Docker, cloud platforms, and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) principles.
Example: DevOps engineers at Netflix ensuring the reliability and scalability of streaming services.
7. Blockchain Developers
Blockchain technology is transforming industries such as finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. Blockchain developers design and implement decentralized applications (DApps), smart contracts, and blockchain-based solutions using platforms like Ethereum or Hyperledger.
Skills Needed: Proficiency in blockchain programming languages like Solidity, knowledge of cryptography, and distributed systems.
Example: Blockchain developers at IBM building enterprise-grade blockchain solutions.
8. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Developers
AR and VR technologies are revolutionizing industries by creating immersive and interactive experiences. AR developers overlay digital content onto the real world, while VR developers design virtual environments.
Skills Needed: Tools like Unity or Unreal Engine for AR/VR application development.
Example: AR/VR developers at Meta Platforms creating VR experiences for Oculus headsets and AR features for social media.
 9. Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists
9. Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists
The IoT connects billions of devices, driving demand for professionals who can design, develop, and manage IoT ecosystems. IoT specialists work on hardware design, firmware development, and platform integration to enable communication between connected devices.
Skills Needed: Knowledge of embedded systems, wireless communication protocols, and cloud computing.
Example: Hyphen Deux is currently hiring for various positions to develop our first chip, Asterix – a microcontroller designed for IoT, automotive, and industrial applications. Join us to be part of this exciting journey! Explore opportunities with us.
10. Robotics Engineers
Advancements in robotics and automation are creating opportunities for robotics engineers to design and develop robotic systems. They design hardware, develop control algorithms, and integrate sensors for perception and navigation.
Skills Needed: Expertise in robotics, mechatronics, computer vision, and programming languages like C++ or Python.
Example: Robotics engineers at Boston Dynamics developing agile and versatile robots for various applications.
Conclusion
As technology continues to evolve and reshape industries, the demand for skilled tech professionals will grow. The technology jobs outlined in this guide offer promising career opportunities with significant growth potential and the chance to make a meaningful impact. By acquiring the necessary skills, staying updated on emerging technologies, and adapting to evolving roles, aspiring tech professionals can thrive in the dynamic tech industry of the future.
Source: techovedas

 Microcontroller: The Body
Microcontroller: The Body




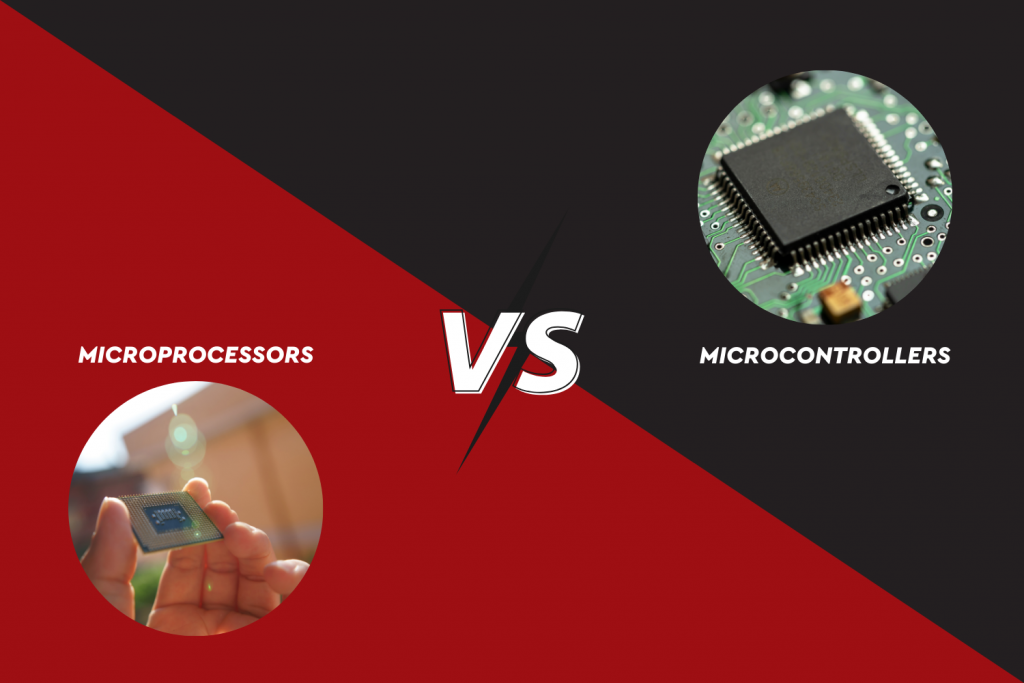
 2. Cybersecurity Analysts and Ethical Hackers
2. Cybersecurity Analysts and Ethical Hackers 9. Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists
9. Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists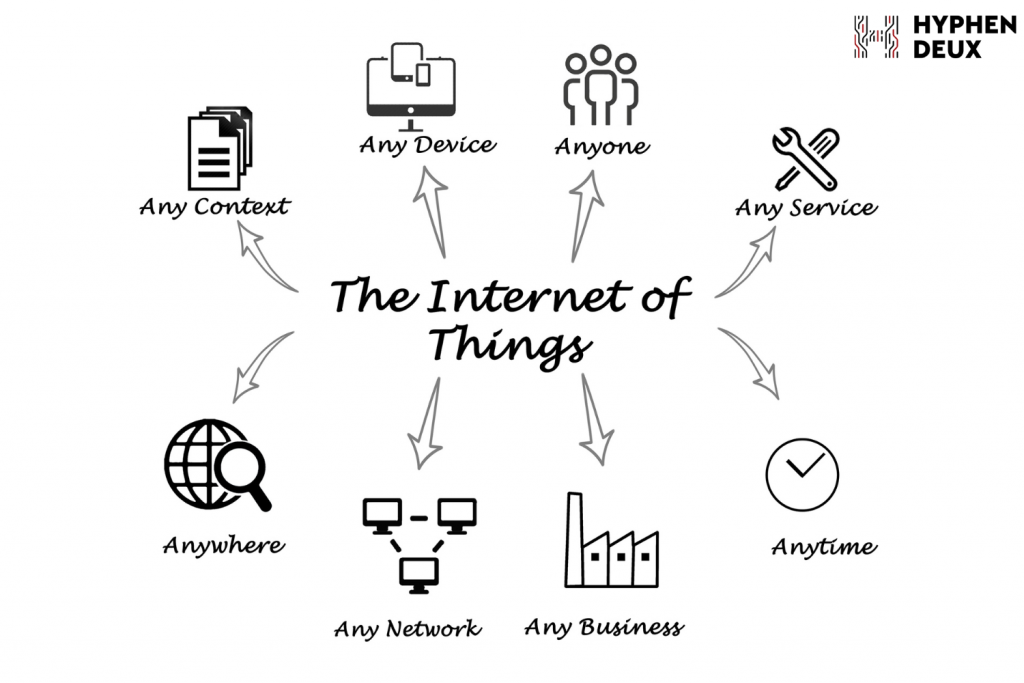
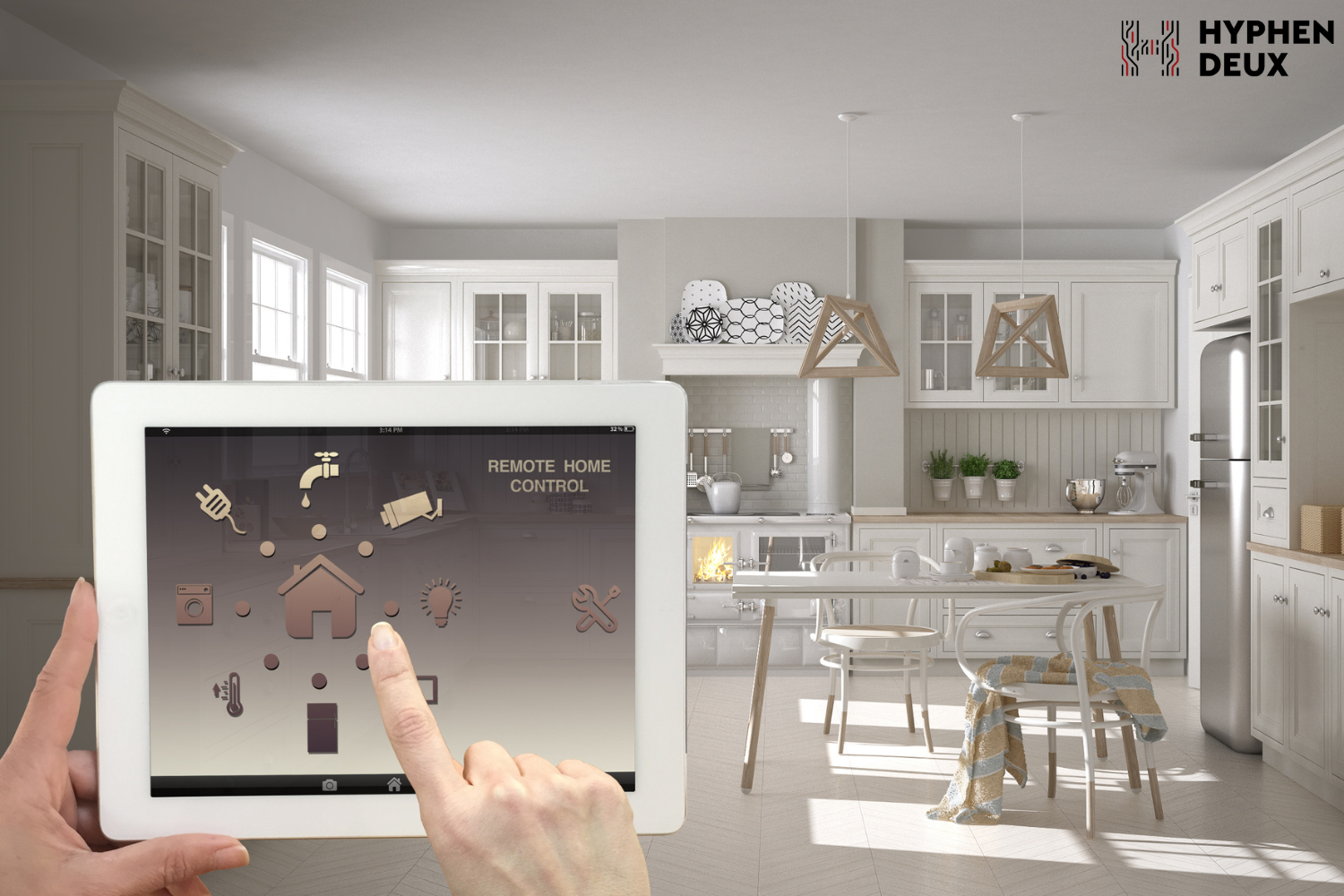 Smart home
Smart home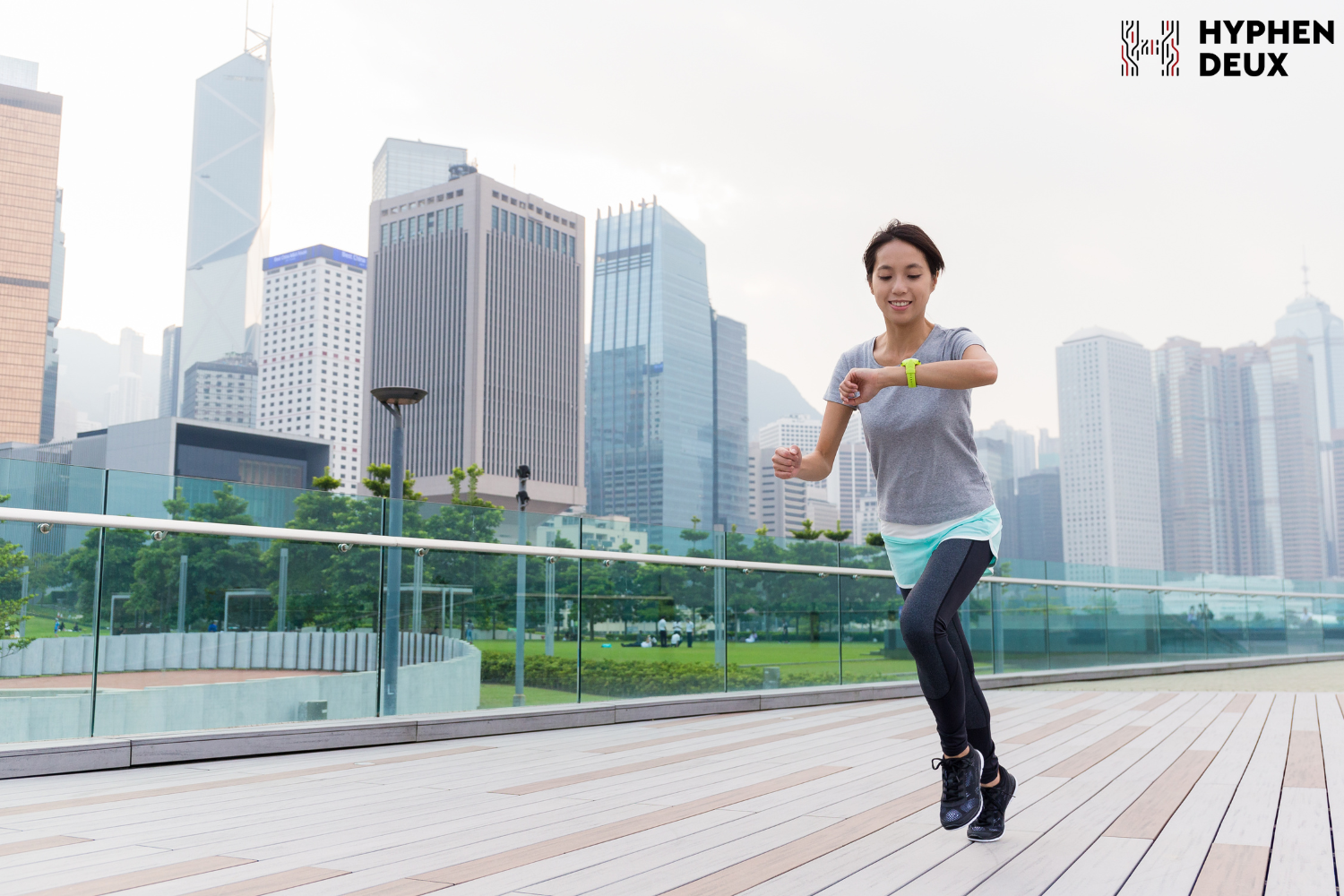 Wearable technology has evolved to include energy-efficient, data-collecting devices. From fitness bands measuring heart rates and calories to smartwatches providing real-time alerts, wearables now incorporate advanced features such as blood pressure monitoring and electrocardiogram (ECG) readings, enhancing health tracking and overall user experience.
Wearable technology has evolved to include energy-efficient, data-collecting devices. From fitness bands measuring heart rates and calories to smartwatches providing real-time alerts, wearables now incorporate advanced features such as blood pressure monitoring and electrocardiogram (ECG) readings, enhancing health tracking and overall user experience. Smart cities are transforming urban living through optimized traffic systems and enhanced services. IoT applications include smart surveillance for public safety, automated transportation for efficient mobility, and energy management for sustainability. Waste management systems and environmental monitoring contribute to cleaner and more sustainable urban environments.
Smart cities are transforming urban living through optimized traffic systems and enhanced services. IoT applications include smart surveillance for public safety, automated transportation for efficient mobility, and energy management for sustainability. Waste management systems and environmental monitoring contribute to cleaner and more sustainable urban environments.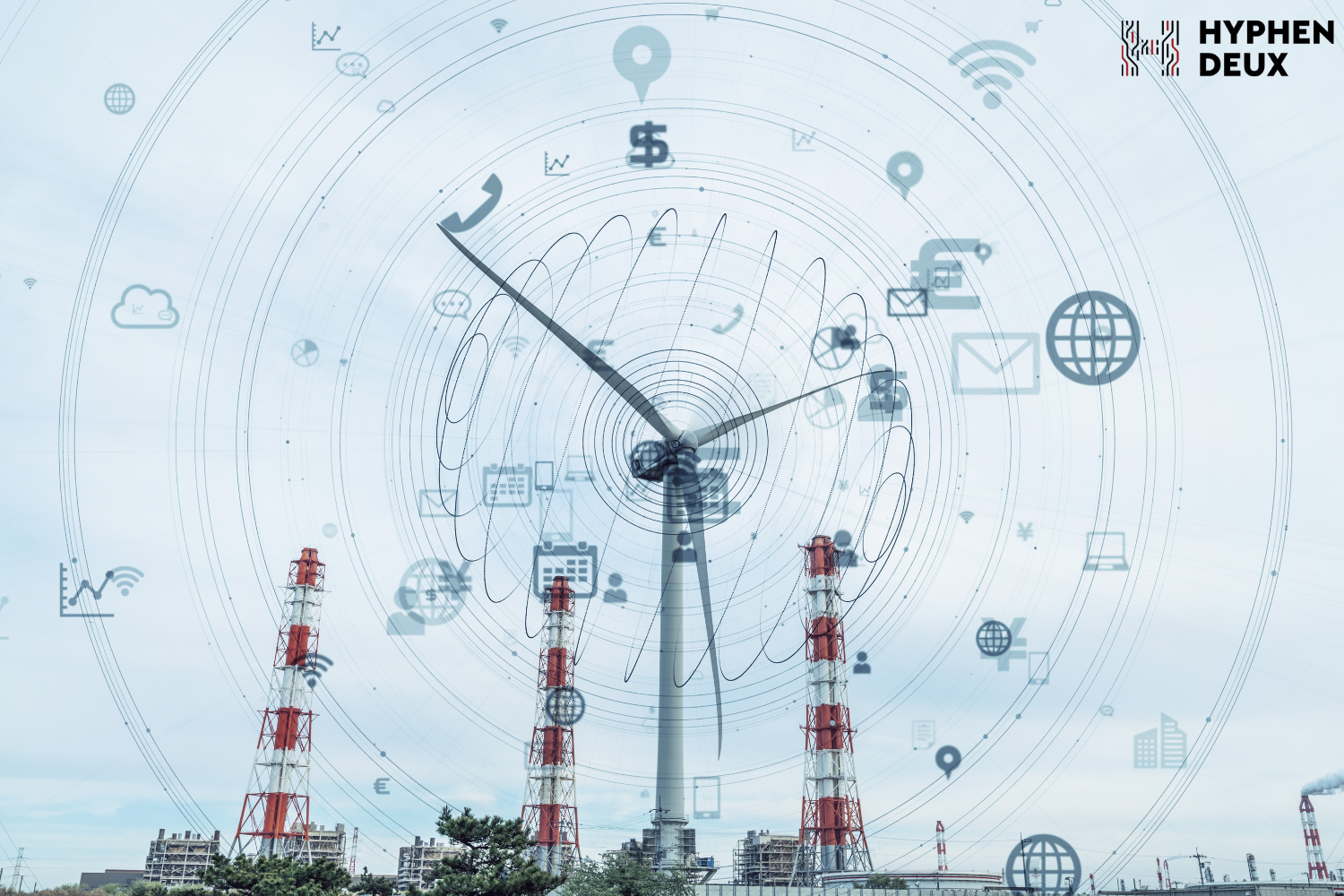 Industrial IoT
Industrial IoT The automotive industry is rapidly transforming with connected cars offering enhanced safety and connectivity. Features include real-time alerts for drivers, advanced in-car entertainment, and autonomous driving capabilities, making driving safer and more enjoyable. IoT integration in connected cars extends beyond safety, contributing to traffic management through vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication.
The automotive industry is rapidly transforming with connected cars offering enhanced safety and connectivity. Features include real-time alerts for drivers, advanced in-car entertainment, and autonomous driving capabilities, making driving safer and more enjoyable. IoT integration in connected cars extends beyond safety, contributing to traffic management through vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication.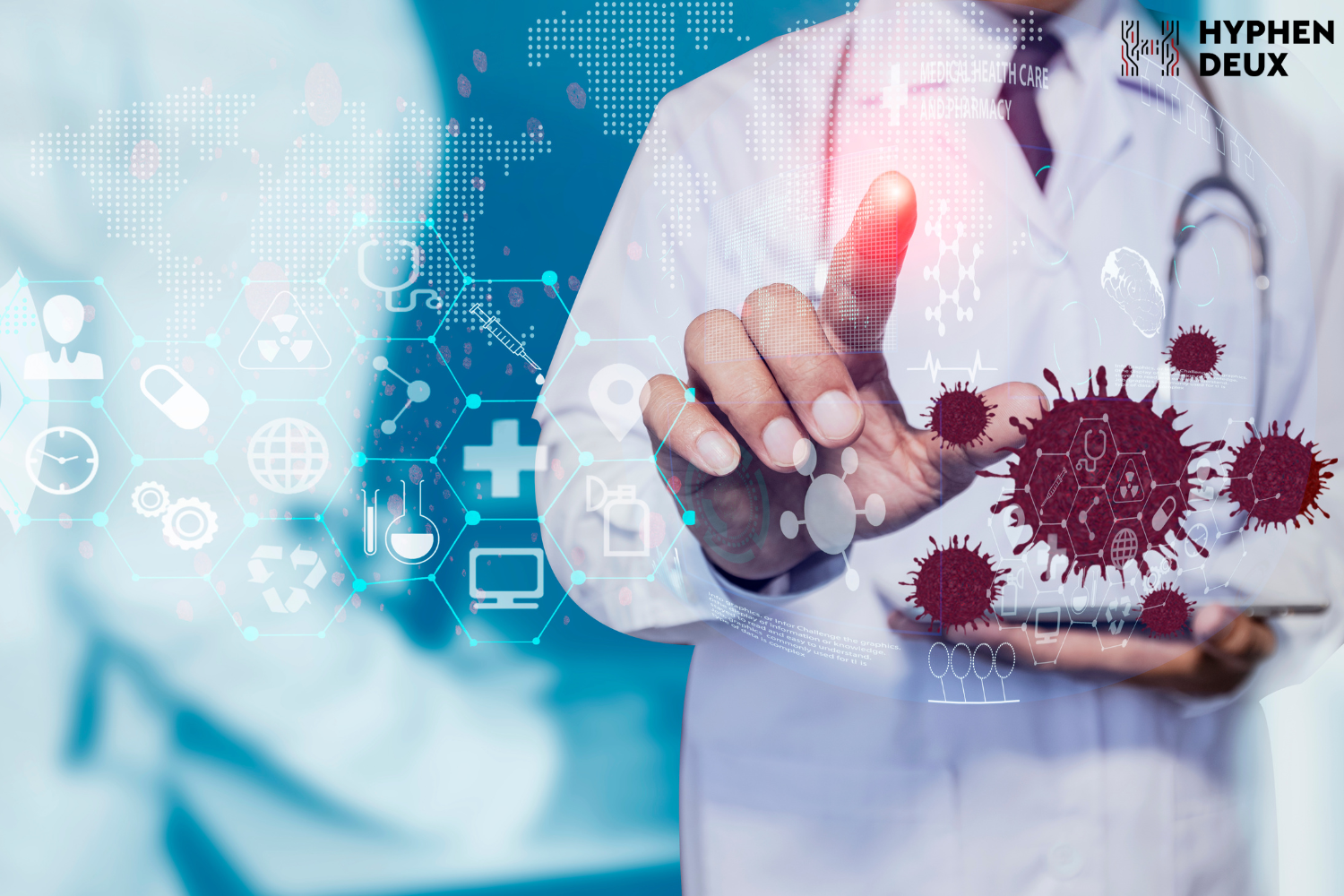 IoT is positively influencing patient care with continuous monitoring and automated alerts. Wearables, IoT devices, and smart beds equipped with sensors enhance healthcare delivery by providing real-time health information and facilitating easy access to patient history. IoT in healthcare extends to remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and IoT-enabled medical devices such as insulin pumps and pacemakers.
IoT is positively influencing patient care with continuous monitoring and automated alerts. Wearables, IoT devices, and smart beds equipped with sensors enhance healthcare delivery by providing real-time health information and facilitating easy access to patient history. IoT in healthcare extends to remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and IoT-enabled medical devices such as insulin pumps and pacemakers.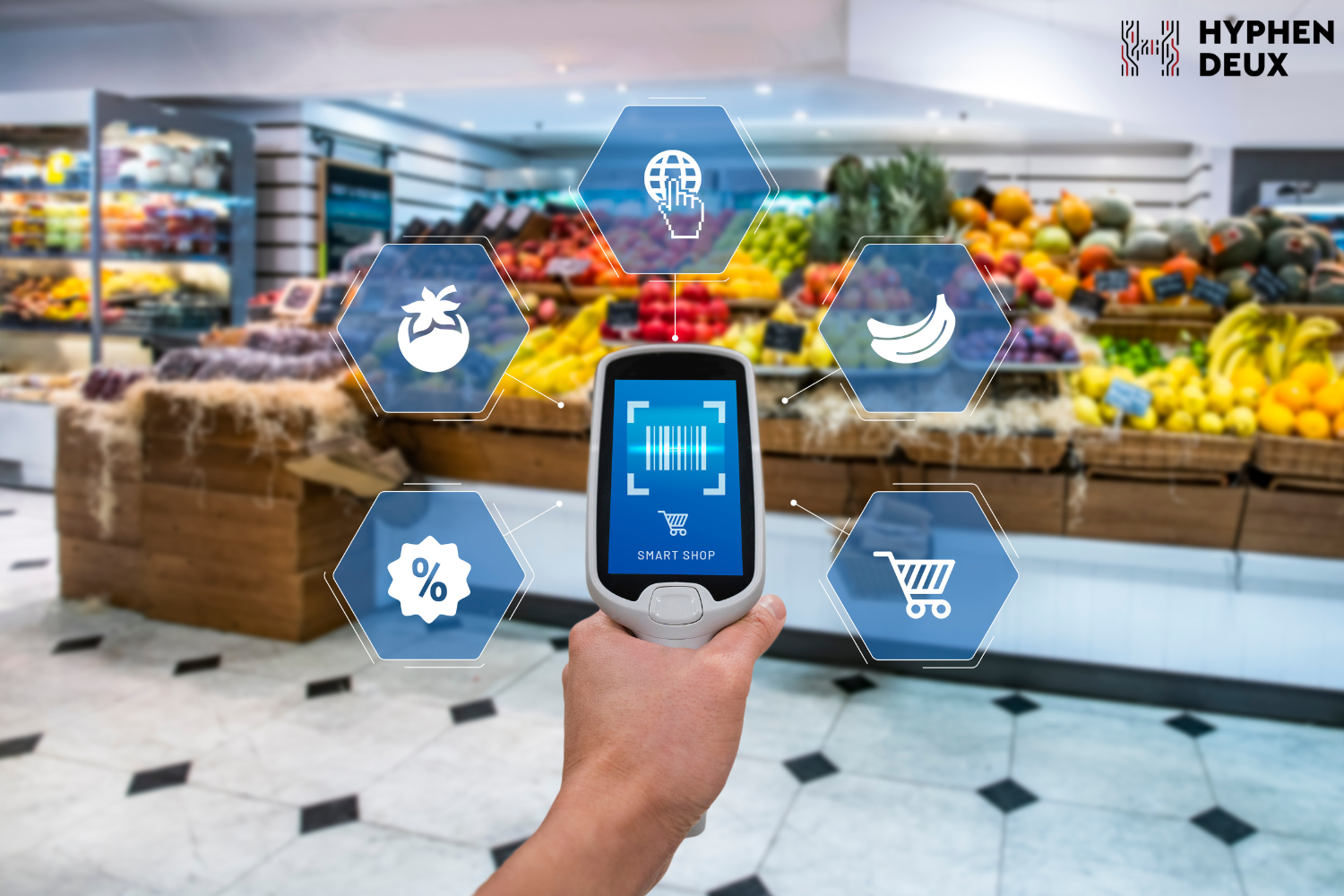 Retail experiences are elevated with IoT applications, offering quick and efficient in-store checkout. RFID technology reads product tags, enabling seamless transactions, and beacon systems enhance customer engagement by providing personalized offers based on location. Advanced inventory management systems using IoT reduce stockouts and optimize supply chains for retailers.
Retail experiences are elevated with IoT applications, offering quick and efficient in-store checkout. RFID technology reads product tags, enabling seamless transactions, and beacon systems enhance customer engagement by providing personalized offers based on location. Advanced inventory management systems using IoT reduce stockouts and optimize supply chains for retailers.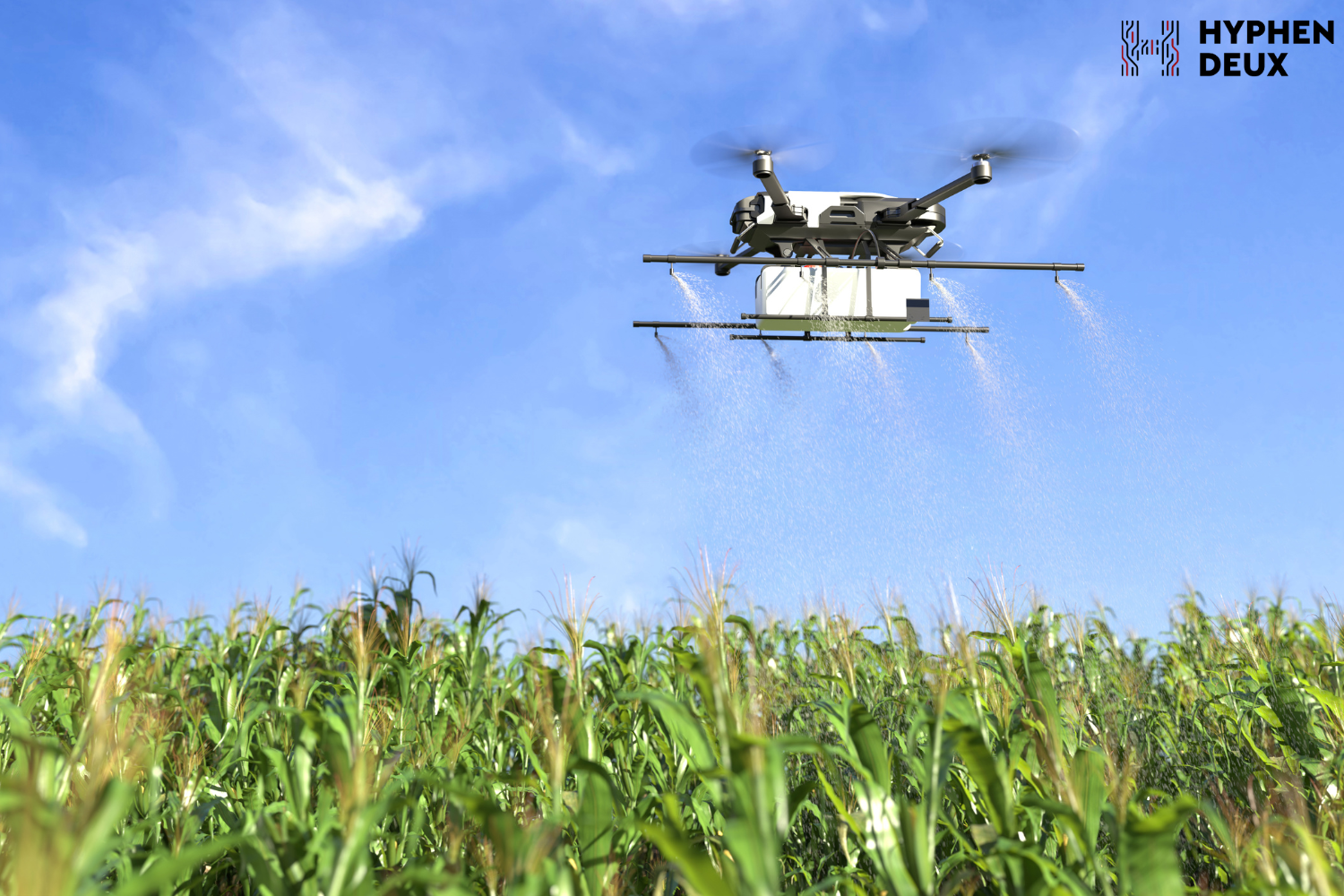 IoT empowers farmers with data-driven decisions for improved productivity. Soil condition monitoring, weather data analysis, and smart farming technologies enhance crop yield by providing insights into irrigation planning, optimal planting times, and disease prevention. Drones equipped with IoT sensors contribute to precision agriculture, enabling farmers to monitor large fields more effectively.
IoT empowers farmers with data-driven decisions for improved productivity. Soil condition monitoring, weather data analysis, and smart farming technologies enhance crop yield by providing insights into irrigation planning, optimal planting times, and disease prevention. Drones equipped with IoT sensors contribute to precision agriculture, enabling farmers to monitor large fields more effectively.