14 Semiconductor Terms Everyone Should Know
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 1.1 Semiconductor
- 1.2 Transistor
- 1.3 3. Integrated Circuit (IC)
- 1.4 Diode
- 1.5
- 1.6 CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)
- 1.7 Fabrication Process
- 1.8
- 1.9 Moore’s Law
- 1.10 Logic, Memory, and Analog Chips
- 1.11 VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration)
- 1.12 Process Node
- 1.13 Assembly
- 1.14 Fab (Fabrication)
- 1.15 Fabless Company
- 1.16 OSATs (Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test)
- 2 Conclusion
Introduction
-
Semiconductor
Semiconductors are materials with electrical conductivity levels between those of conductors and insulators. This unique property allows them to selectively conduct electrical currents, making them ideal for use in electronic devices. Silicon (Si) is the most widely used material in the electronics industry due to its abundance and suitable properties. Silicon wafers serve as the canvas upon which integrated circuits are fabricated.
-
Transistor
One of the most transformative inventions of the 20th century, the transistor revolutionized electronics by amplifying and switching electronic signals. Its invention paved the way for the miniaturization of electronic devices and laid the foundation for integrated circuits.
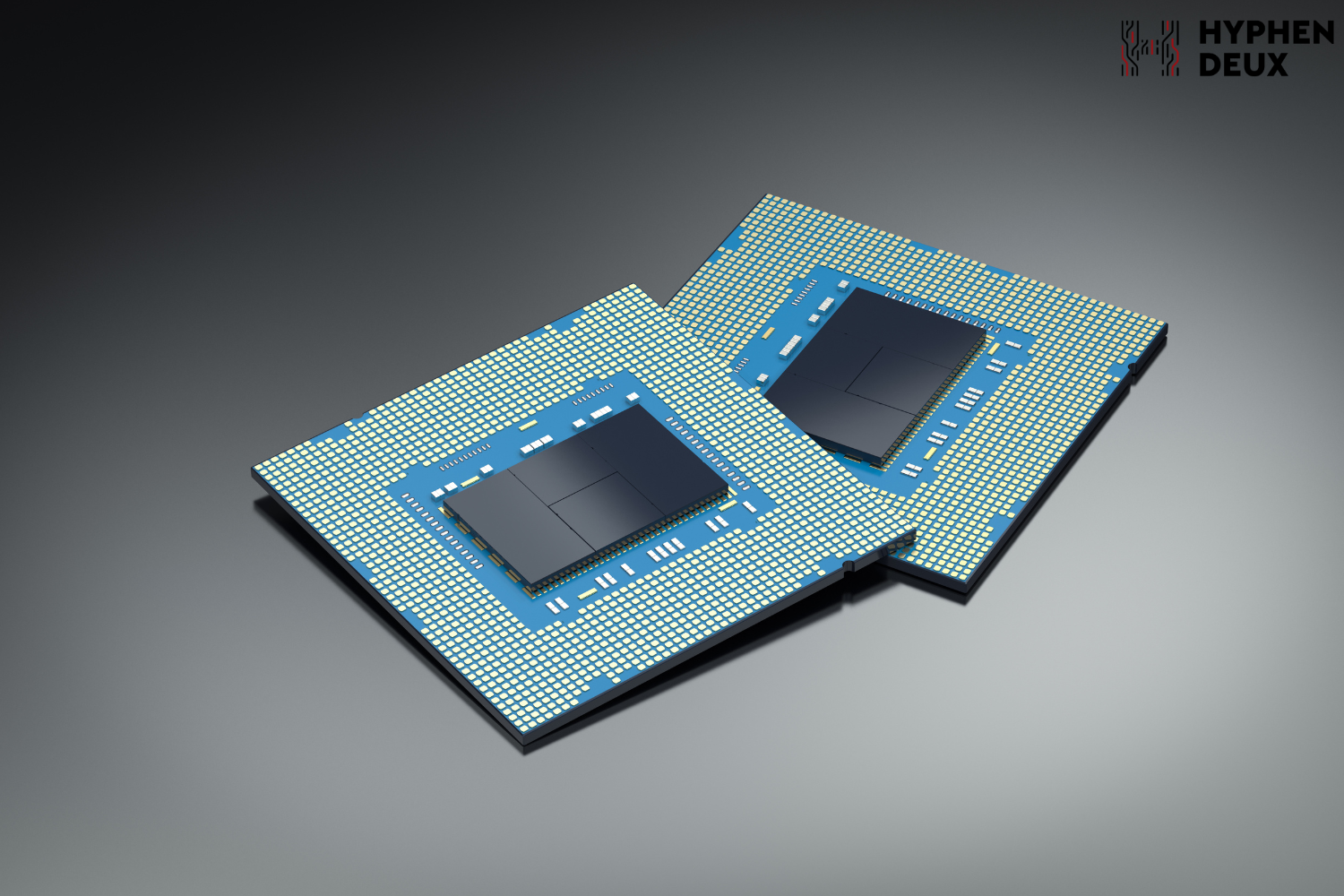
3. Integrated Circuit (IC)
Integrated circuits, often referred to as microchips, are the epitome of semiconductor technology. Engineers etch these complex assemblies of electronic components onto a small flat piece of semiconductor material, enabling the creation of highly functional electronic systems in a compact form factor.
-
Diode
Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in one direction only. Widely used as rectifiers in power supplies and as switching elements in electronic circuits, diodes play a crucial role in directing the flow of electrical currents within electronic systems.
-
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)
CMOS technology represents a cornerstone of modern integrated circuit design. Renowned for its low power consumption and high noise immunity, CMOS technology is ubiquitous in digital circuits, powering everything from microprocessors to memory chips.
-
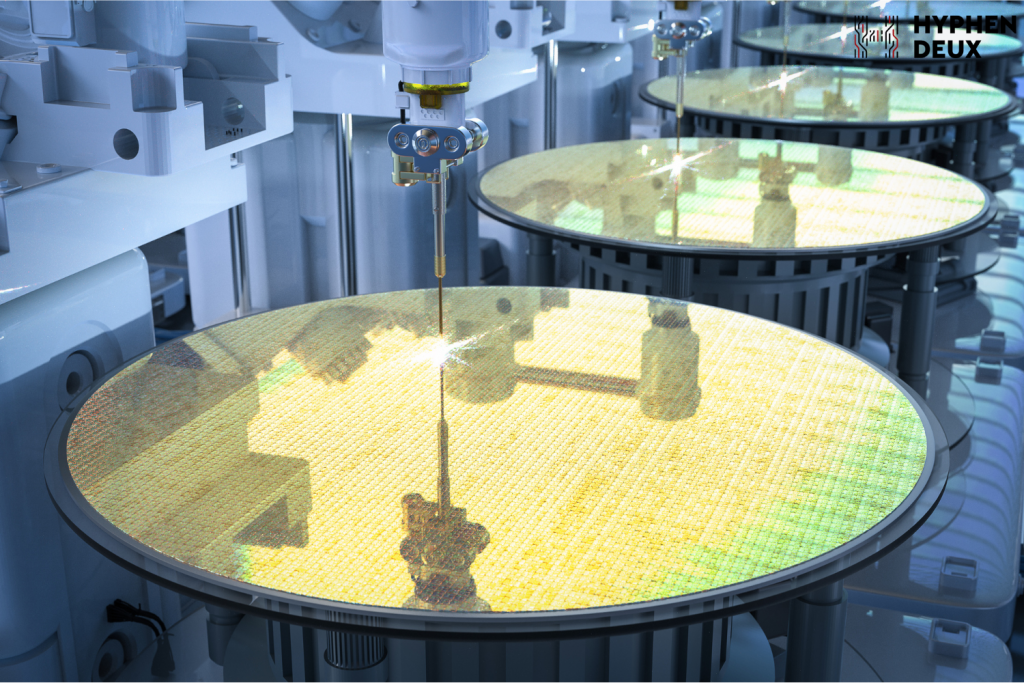
Fabrication Process
The fabrication process encompasses a series of meticulously orchestrated steps aimed at creating integrated circuits on wafers. From deposition and lithography to etching and doping, each stage of the process plays a crucial role in shaping the final functionality and performance of the resulting microchips.
-
Moore’s Law
Moore’s Law, although not a physical law, has served as a guiding principle for the semiconductor industry for several decades. This empirical observation predicts that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles approximately every two years, driving continuous advancements in computing power, cost reduction, and miniaturization.
-
Logic, Memory, and Analog Chips
Logic chips process digital signals using Boolean logic functions, memory chips store and retrieve digital data efficiently, and analog chips bridge the gap between digital and analog domains, enabling the processing and conversion of signals between these two realms. Together, these semiconductor devices form the foundation of modern electronic systems, powering everything from computers and smartphones to complex industrial automation and communication networks.
-
VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration)
VLSI technology represents the pinnacle of semiconductor integration, enabling the creation of complex electronic systems by integrating thousands or even millions of transistors onto a single chip. This technology has revolutionized industries ranging from telecommunications to automotive electronics, empowering the development of innovative and feature-rich electronic devices.
-
Process Node
The term “process node” refers to the size of the smallest feature that can be created on a chip during the manufacturing process. Measured in nanometers, process nodes signify the level of miniaturization achieved in chip fabrication. Smaller process nodes enable the production of devices with higher performance, lower power consumption, and reduced manufacturing costs, driving the relentless march of technological progress.
-
Assembly
Assembly involves the integration of individual semiconductor components into functional electronic systems. This process encompasses die attach, wire bonding, encapsulation, and other techniques aimed at ensuring the reliability and performance of the final product. Advanced assembly technologies, such as flip-chip bonding and wafer-level packaging, enable the creation of compact, high-performance devices suited for a wide range of applications.
-
Fab (Fabrication)
Semiconductor fabrication, often referred to as “Fab,” encompasses the complex series of processes involved in creating integrated circuits on wafers. These processes include photolithography, etching, deposition, doping, and more, each meticulously orchestrated to achieve precise control over device geometry and electrical properties. Advanced fabrication facilities, equipped with state-of-the-art equipment and cleanroom environments, enable the production of cutting-edge semiconductor devices with nanometer-scale features.
-
Fabless Company
Fabless companies innovate, design, and market microchips while outsourcing wafer processing, packaging, and testing to third-party partners. They partner with foundries such as TSMC and GlobalFoundries to print designs on wafers and contract out testing and packaging services to outsourced semiconductor assembly and testing (OSAT) providers. Clients of fabless companies are original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) or end-user device innovators incorporating microchips into their products.
Hyphen Deux is a prominent Vietnamese IC Design specializing in microcontrollers for IoT, automotive, industrial, and AI chips.
-
OSATs (Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test)
OSATs play a crucial role in the supply chain, providing essential services like packaging, testing, and logistics. As manufacturing has become more specialized and capital-intensive, many companies choose to outsource assembly and testing processes to OSATs. These specialized firms leverage economies of scale and expertise to deliver high-quality, cost-effective solutions, allowing companies to focus on core competencies such as design and fabrication.
Conclusion
From the humble beginnings of the transistor to the intricate complexities of VLSI design, the evolution of semiconductor engineering continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible in the realm of electronics. Understanding these fundamental semiconductor terms is essential for anyone looking to grasp the intricacies of the semiconductor industry.
Source: techovedas
Follow us on LinkedIn

